Pythagorean theorem the well-known geometric theorem that the sum of the squares on the legs of a right triangle is equal to the square on the hypotenuse the side opposite the right angleor in familiar algebraic notation a2 b2 c2. The Pythagorean Theorem is a mathematical law that states that the sum of the square of the lengths of the two short sides of the right triangle is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse.

Which Of The Following States The Pythagorean Theorem Brainly Com
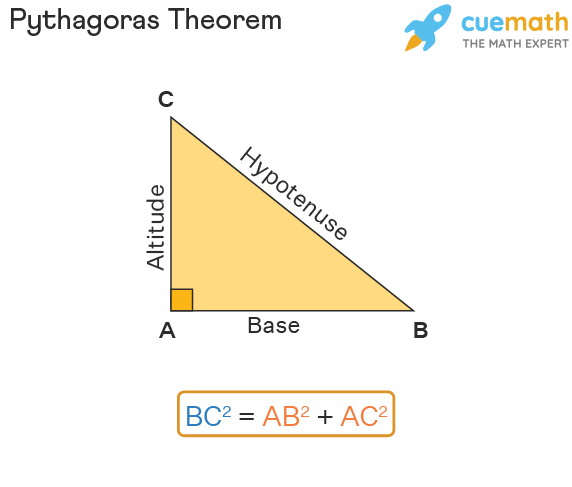
In a right triangle the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the legs.

. Part IState the equation that relates arc length to central angle4 points Arc length rtheta. Hence the hypotenuse of the triangle is 1077 cm. If csquared is less than asquared plus bsquared then the triangle is obtuse.
In a right triangle the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the legs. The legs have length 24 and X are the legs. The Pythagorean Theorem states that in any right triangle the sum of the squares of the lengths of the triangles legs is the same as the square of the length of the triangles hypotenuse.
How do you find the hypotenuse in the 30-60-90 theorem. The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle the sum of the squares of the legs equals the square of the hypotenuse. If a triangle is right-angled 90 degrees the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides according to Pythagoras theorem.
A 5 in. Written by the Greek mathematician Pythagoras the Pythagorean theorem states that in right triangles the sum of the squares of the two legs is equal to the square of the hypotenuse. Find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle if the lengths of the other two sides are 3 inches and 4 inches.
The Pythagorean Theorem can be used when we know the length of two sides of a right triangle and we need to get the length of the third side. To solve problems that use the Pythagorean Theorem we will need to find square roots. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to see if the measurements below can form a right triangle.
C 13 in. Use the Pythagorean theorem to determine the length of X. A 2 b 2 c 2.
C2 a2 b2. B 12 in. Where a and b are the legs of a right triangle and c is the hypotenuse.
The Pythagorean Theorem shows the relationship between the sides of a right triangle. No it is not a right triangle. The area of the square built upon the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares upon the remaining sides Figure 1.
The hypotenuse is 26. The Pythagoras theorem also known as the Pythagorean theorem states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the lengths of other two sides of the right-angled triangle. Identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle.
There is not enough info. What theorem goes with the following formula. The formula for the Pythagorean theorem is a2b2c2 where a and b are the legs of a right triangle and c is the hypotenuse.
The result of multiplying a number by itself. A2 b2 c2 a 2 b 2 c 2. This theorem is represented by the formula.
According to the definition the Pythagoras Theorem formula is given as. If you multiply all 3 numbers in a Pythagorean triple by the same whole number then the three new numbers will form a pythagorean triple. In a right triangle the.
According to the Pythagorean Theorem the sum of the areas of the two red squares squares A and B is equal to the area of the blue square square C. Answered expert verified. A 2 b 2 c 2.
In a right triangle the. The hypotenuse is red in the diagram below. The Pythagorean Theorem states that the sum of the squared sides of a right triangle equals the length of the hypotenuse squared.
Which of the following states the pythagorean theorem. Part IIFind the angle in radians4 points theta will. Put simply if you know the lengths of two sides of a right triangle you can apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the third side.
The Pythagoras Theorem states that in a right-angled triangle the sum of the square of the base and the square of the perpendicular is equal to the square of the hypotenuse. This is illustrated at the picture on the right. The purpose of this assignment is to help you practice the following.
Hypotenuse2 Perpendicular2 Base2. Angle at the Apex of a Cone Purpose. So the area of the large square is.
In a right triangle the square of the hypotenuse equals the sum of the legs. If you know the length of any 2 sides of a right triangle you can use the Pythagorean equation formula to find the length of the third side. This assignment will help you to become familiar with the following important content knowledge in trigonometry Know and use the are length and sector area formulas.
Where c c is the length of the hypotenuse a a and b b are the lengths of the legs. In mathematics the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle. C2 a2 b2.
By The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica Edit History. It is always opposite of and never is a part of the right angle. If m n2 then m n for n 0 If m n 2 then.
State and apply Pythagorean Theorem. In Simplify and Use Square Roots we introduced the notation m m and defined it in this way. The side opposite to the right angle 90 is the longest side known as Hypotenuse because the side opposite to the greatest angle is the longest.
This is expressed as. It states that for a right triangle the sum of the areas of the squares formed by the legs of the triangle equals the area of the square formed by the triangles hypotenuse. You might recognize this theorem in the form of the Pythagorean equation.
The sum of the squares of the legs of a right triangle is equal to the square of the hypotenuse. Yes it is a right triangle. Arc length r thet a.
This theorem can be written as an equationrelating the leng. The Pythagorean Theorem states that. Or the sum of the squares of the two legs of a right triangle is equal to the square of its hypotenuse.
Write down the formula. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse the side opposite the right angle is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. Substitute values into the formula remember C is the hypotenuse.

Geometry 7 3c Proving The Pythagorean Theorem Using Similar Triangles Youtube

Lesson Explainer Applying The Pythagorean Theorem To Pyramids And Cones Nagwa
Pythagoras Theorem Pythagorean Formula Proof Examples

Which Of The Following States The Pythagorean Theorem A In A Right Triangle The Square Of The Brainly Com
0 Comments